Overview
Brief review of all types of wallets
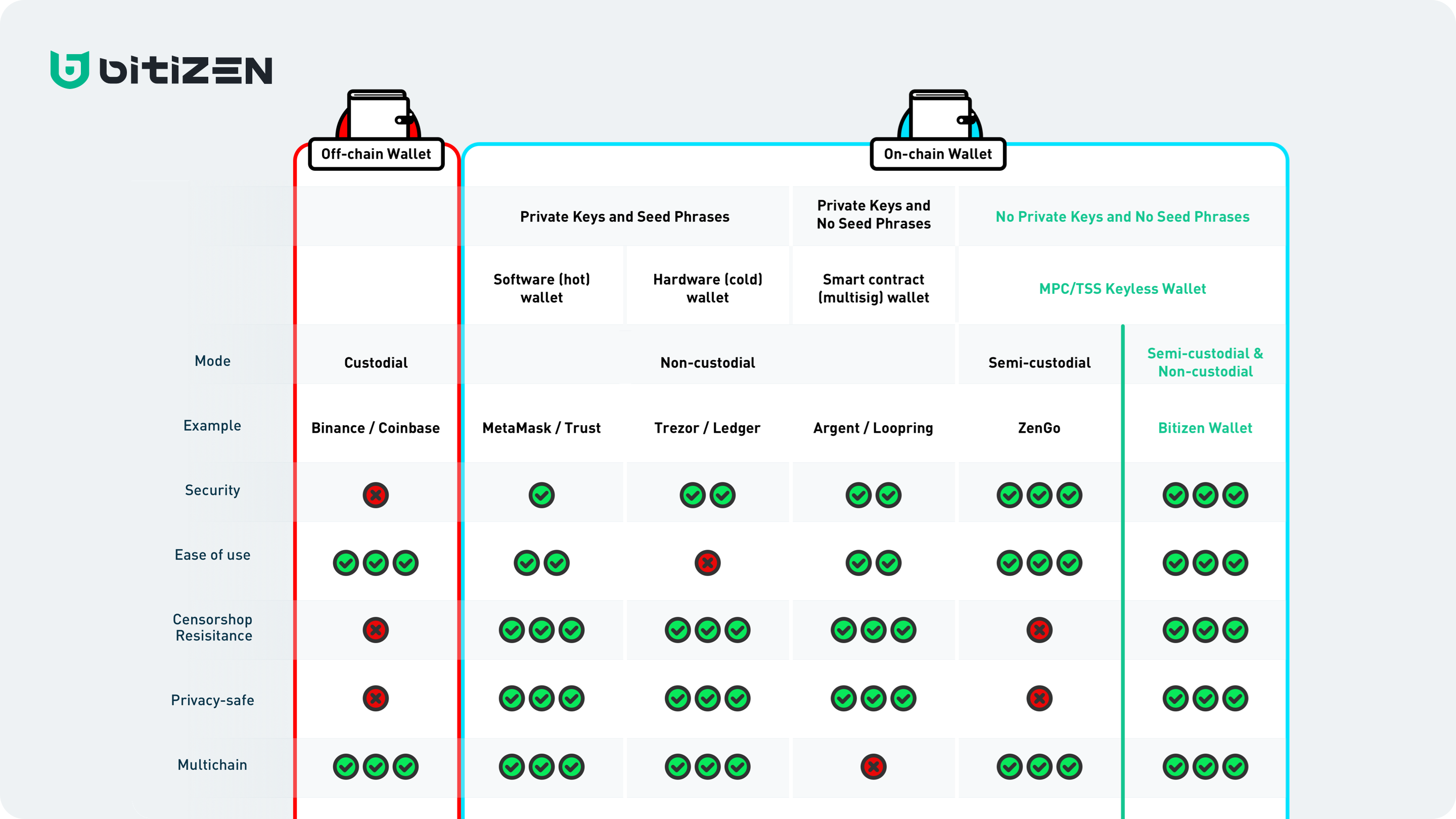
Off-chain Custodial Wallets
Off-chain Custodial wallet is a digital asset management account provided by a third party, for example, a centralized exchange, crypto broker or a custodian service. They can support hundreds of different tokens on all mainstream blockchains, many trading tools and features including P2P exchange, fiat gateways, staking aggregators, data analysis, bonuses etc, providing user-friendly interface and trying to deliver the best service.
They also take the burden of creating accounts and storing crypto for the users, managing the wallets and the private keys. However, centralized exchanges and other custodial services do not give direct access to the crypto for the users; private keys belong not to the users but to the platform operators.
They can easily freeze user accounts and block fund withdrawals for numerous reasons: government regulations, suspicious transactions, KYC requirements, security breaches, insolvency and simply rug pull. This is why the users must consider exchanges and other off-chain custodial services, as not censorship-resistant.
Besides, the exchanges are storing large amounts of crypto of their users, being easy targets for hacker attacks daily, and many of them succeed resulting in losing millions of dollars. Note that exchanges and other services have limited to no responsibility for the loss of funds of their users. We can also consider exchanges as not a secure solution for storing crypto.
On-chain Wallets
All traditional wallets with private keys are non-custodial wallets that can be divided to the three major groups:
- Software (hot) wallets
- Hardware (cold) wallets
- Smart Contract (Multisignature) wallets
Software (hot) wallet is a software for storing or managing private keys on a device which is constantly connected to the Internet. The most common forms of hot wallets are web / desktop / mobile apps / browser extensions.
Many hot wallets are quite simple to use, support many blockchains and let users directly operate their funds. However, having a private key and seed phrase create a single point of failure for such wallets; and even the most popular wallets such as Metamask or Trust wallet are suffering from numerous hacker attacks, and millions of users have already lost all their funds.
No matter how well the software keeps private keys, storing private keys on a device with a connection to the Internet is creating a constant risk for them of being stolen.
Hardware (cold) wallet often refers to hardware devices that store private keys offline; the user needs to connect the hardware device only when signing a transaction. Cold wallets such as Ledger and Trezor are considered to be more secure than hot wallets, however, the user experience is more complicated. Also, a user can still lose the physical device, forget or expose the PIN-code or the seed phrase. Moreover, a user should always carry his hardware device, which is not convenient for daily life or while using Dapps. This is why the cold wallets are having a hard time in mass adoption, and still have the single point of failure of the seed phrases.
Multisignature wallets require multiple parties’ private keys to co-sign a transaction, reducing the risk of a single party being compromised and adding an extra security level. However, multisignature wallets have many disadvantages, such as requiring consensus of the co-signing parties and longer time to finish the signature, exposing relationships between co-signing parties, higher gas fees deducted from each co-signing party, they cannot add or exclude any co-signing parties after the wallet is set; besides, not all blockchain protocols support multisignature contracts, thus seriously limiting the number of supported blockchains, tokens, and Dapps. Multisignature wallets do not have seed phrases, removing the risks related to them; but the signing parties still have their own private keys that should be properly stored and able to get recovered, where the seed phrase may appear again.
Keyless and Seedless Wallets
Keyless and Seedless wallets are the new generation of wallets that are based on MPC-TSS technology. Keyless wallets do not have full private keys at any moment, including wallet creation and signature generation; they neither support seed phrases as a backup and recovery solution. By utilizing cryptographic Secure Multi-Party Computation technology, they generate multiple independent key shares for multiple parties that are used to jointly compute the signature (or, in other words, to co-sign the transaction).
Wallet back-up and recovery solutions via seed phrases are replaced with other mechanisms. For example, 3FA with biometry scan is more secure and familiar for the ordinary Web2 users.